Tuesday, September 23, 2014
Monday, March 31, 2014
Posts by : Admin
13 Natural Home Remedies For Sore Gums
1. Stop brushing with regular over the counter products and make your own paste: 1 cup baking soda, 1 tablespoon hydrogen peroxide, 10 drops of peppermint extract. (Have done this since the late 80s)
2. Make a healing mouthwash with cloves. Cloves help heal toothache and gum pain. Boil one cup of water add 1 tablespoon of cloves and turn off heat. Let it steep for 1 or 2 hours with cloves until cool. Then put in a dark bottle and use it as mouthwash. Great stuff.
3. Up your vitamin C Eat more C-rich foods. It's not just lemons that can help with gum disease, but other foods full of vitamin C such as oranges, grapes, kiwi mango, papaya and strawberry are good choices, too. Vitamin C is an antioxidant, and antioxidants are found to promote connective tissue growth and bone regeneration, which can be affected by various gum problems.
4 The best product that gives relief is a combination of vinegar (Balsamic is the best) and salt. Depending on how severe the pain is you might want to make a facial mask of the vinegar and salt, and apply it to the affected area. This should give you 24 hour comfort. It will expel the topical bacteria surrounding the inflamed area. However, until you remove every chip, from broken teeth, foreign particle or tarter, the pain will reoccur.
5. Put vanilla extract on the area of where the gums are hurting.
6. Take supplements and eat foods that boost the immune system (Echinacea, Lysine, Goldenseal, garlic). Apply tea tree oil to the infection. Use mouthwash several times daily, preferably something that's not too harsh. I like Desert Essence's stuff, especially the kind that contains tea tree oil. Biotene is also good, or you can just gargle with an equal mixture of hydrogen peroxide and water.
7. Wintergreen Oil is the only thing that helped me when I had severe gum pain.
8. Make a sea salt solution. Dissolve a small amount of sea salt in a cup of warm water. Swish a sip of the solution in your mouth for 30 seconds and spit it out. Repeat several times. Salt water will reduce swollen gums and draw infection out of any abscesses. Add this mouth rinse to your twice-daily brushing routine.
9. Apply tea bags. Steep a tea bag in boiling water, remove and allow it to cool until you can handle it comfortably. Hold the cooled tea bag on the affected area of your gums and keep it there for about five minutes. The tannic acid in the tea bag can work effectively to relieve gum infection. Directly applying the tea bag to your gums is more effective than simply drinking the beverage. Plus, drinking too much tea has a dental downside: discolored, tea-stained teeth.
10. Rub some honey. Honey has natural antibacterial and antiseptic properties, so you can put it to work treating your infected gums. Once you brush your teeth, rub a small amount of honey on the problem area of your gums. Given honey's high sugar content, you want to be careful you don't overapply it and do your best to put it on your gums only rather than on your teeth.
11. Drink cranberry juice. Cranberry juice can prevent bacteria from sticking to your teeth, so try drinking up to 4 ounces of the unsweetened juice daily.
12. Make a lemon paste. Make a paste from the juice of one lemon and some salt. Mix it well and apply to your teeth. Let it sit for a few minutes and gargle with warm water to rinse it off. Lemons offer a win-win solution for treating gum disease. First, they're an anti-inflammatory, which makes them helpful in treating infected gums. Not only that, but lemons contain vitamin C, which can help your gums fight off infection.
13. Increase your intake of vitamin D. Vitamin D has anti-inflammatory properties, so be sure you're getting enough of this vitamin when you're trying to heal swollen gums and prevent the condition from reoccurring. Older adults should particularly take note of this vitamin. According to the National Institutes of Health, higher blood levels of vitamin D seem to be linked to a reduced risk of gum disease in people age 50 and older. Get your vitamin D fix by soaking up the sun at least 15 to 20 minutes twice a week and eating D-rich foods such as salmon, whole eggs and cod liver oil.
Thursday, February 20, 2014
Posts by : Admin
When Food Supplies Are Low
If activity is reduced, healthy people can survive on half their usual
food intake for an extended period and without any food for many days.
Food, unlike water, may be rationed safely, except for children and pregnant
women.
If your water supply is limited, try to avoid foods that are high in fat and protein, and don’t
stock salty foods, since they will make you thirsty. Try to eat salt-free
crackers, whole grain cereals and canned foods with high liquid content.
You don’t need to go out and buy unfamiliar foods to prepare an emergency food supply. You
can use the canned foods, dry mixes and other staples on your cupboard shelves. In fact, familiar foods are important. They can lift morale and give a feeling of security in time of stress. Also, canned foods won’t
require cooking, water or special preparation.
As you stock food, take into account your family’s unique needs and tastes.
Try to include foods that they will enjoy and that are also high in calories
and nutrition. Foods that require no refrigeration, preparation or cooking
are best.
manual can opener
and elderly people. Nursing mothers may need liquid formula, in case they are unable to nurse. Canned dietetic foods, juices and soups may be helpful for ill or elderly people.
rawhide
foods for your pets.
How to Cook If the Power Goes Out
For emergency cooking you can use a fireplace, or a charcoal grill or campstove can be used outdoors. You can also heat food with candle warmers, chafing dishes and fondue pots. Canned food can be eaten right out of the can. If you heat it in the can, be sure to open the can and remove the label first.
Short-Term Food Supplies
Even though it is unlikely that an emergency would cut off your food supply
for two weeks, you should prepare a supply that will last that long.
The easiest way to develop a two-week stockpile is to increase the amount of basic foods
you normally keep on your shelves.
Storage Tips
Keep food in a dry, cool spot – a dark area if possible.
Keep food covered at all times.
Open food boxes or cans care-fully so that you can close them tightly after each use.
Wrap cookies and crackers in plastic bags, and keep them in tight containers.
Empty opened packages of sugar, dried fruits and nuts into screw-top jars or air-tight cans
to protect them from pests.
Inspect all food for signs of spoilage before use.
Use foods before they go bad, and replace them with fresh supplies, dated with ink or
marker. Place new items at the back of the storage area and older ones
in front.
Nutrition Tips
During and right after a disaster, it will be vital that you maintain your strength.
So remember:
Eat at least one well-balanced meal each day.
Drink enough liquid to enable your body to function properly (two quarts a day).
Take in enough calories to enable you to do any necessary work.
Include vitamin, mineral and protein supplements in your stockpile to assure adequate
nutrition.
How long can food supplies be stored?
To judge how long you can store food supplies, look for an “expiration date” or “best if used by” date on the product. If you can not find a date on the product, then the general recommendation is to store food products for six months and then replace them.
Some households find it helpful to pull food products for their regular meals from their disaster supplies kit and replace them immediately on an ongoing basis, so the food supplies are always fresh.
What kinds of food supplies are recommended to store in case of a disaster?
Try to avoid foods that are high in fat and protein, and don’t stock salty
foods, since they will make you thirsty. Familiar foods can lift morale
and give a feeling of security in time of stress. Also, canned foods won’t
require cooking, water or special preparation. Take into account your
family’s unique needs and tastes. Try to include foods that they will
enjoy and that are also high in calories and nutrition.
Store supplies of non-perishable foods and water in a handy place. You need to have these
items packed and ready in case there is no time to gather food from the kitchen when disaster strikes. Sufficient supplies to last several days to a week are recommended.
Select foods that require no refrigeration, preparation or cooking, and little or no water.
Foods that are compact and lightweight are easy to store and carry.
Try to eat salt-free crackers, whole grain cereals and canned food with high liquid content.
Recommended foods include:
Ready-to-eat canned meats, fruits and vegetables. (Be sure to include a manual can opener)
Canned juices, milk and soup (if powdered, store extra water).
High energy foods, such as peanut butter, jelly, crackers, granola bars and trail mix.
Comfort foods, such as hard candy, sweetened cereals, candy bars and cookies.
Instant coffee, tea bags.
Foods for infants, elderly persons or persons on special diets, if necessary.
Compressed food bars. They store well, are lightweight, taste good and are nutritious.
Trail mix. It is available as a prepackaged product or you can assemble it on your own.
Dried foods. They can be nutritious and satisfying, but have some have a lot of salt content,
which promotes thirst. Read the label.
Freeze-dried foods. They are tasty and lightweight, but will need water for reconstitution.
Instant Meals. Cups of noodles or cups of soup are a good addition, although they need
water for reconstitution.
Snack-sized canned goods. Good because they generally have pull-top lids or twist-open
keys.
Prepackaged beverages. Those in foil packets and foil-lined boxes are suitable because they
are tightly sealed and will keep for a long time.
Food Options to Avoid:
Commercially dehydrated foods. They can require a great deal of water for reconstitution and
extra effort in preparation.
Bottled foods. They are generally too heavy and bulky, and break easily.
Meal-sized canned foods. They are usually bulky and heavy.
Whole grains, beans, pasta. Preparation could be complicated under the circumstances of a
disaster.
Shelf-life of Foods for Storage
Here are some general guidelines for rotating common emergency foods.
Use within six months:
powdered milk
Dried fruit (in metal container)
Dry, crisp crackers
(in metal container)
Potatoes
Use within one year:
Canned condensed meat and vegetable soups
Canned fruits, fruit juices and vegetables
Ready-to-eat cereals and uncooked instant cereals (in metal containers)
Peanut butter
Jelly
Hard candy and canned nuts
Vitamin C
May be stored indefinitely
(in proper containers and conditions):
Wheat
Vegetable oils
Dried corn
Baking powder
Soybeans
Instant coffee, tea and cocoa
Salt
Noncarbonated soft drinks
White rice
Bouillon products
Dry pasta
Powdered milk (in nitrogen-packed cans)
Sunday, February 16, 2014
Posts by : Admin
Beets
Benefits of Beet Juice
Beets are a fabulous root vegetable and the benefits of beet juice are plenty. Beets have been used traditionally to heal people.
Traditional Benefits
According to Wikipedia ancient Romans used beetroot as a treatment for fevers and constipation. Hippocrates - the father of medicine - advocated the use of beet leaves as binding for wounds. From the Middle Ages, beetroot was used as a treatment for a variety of conditions, especially illnesses relating to digestion and the blood.
Betalain
One of the major benefits of beet juice it that it contains a color pigment called betalain. This is a powerful antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, fungicidal and aid in detoxification substance. There is research that indicates that betalain may exhibit anti-cancer activity.
Betalains may occur in any part of the plant, including the petals of flowers, fruits, leaves, stems, and roots.
Nutritional Value of Beets
Beets with roots
Beet roots are high in folic acid and manganese. The green leafs are high in vitamin A (127% RDA), Vitamin C (50% RDA), vitamin K (500% RDA) as well as calcium, iron, magnesium, potassium, copper and magnesium, sulfur, silica and choline.
Traditionally, people use beet juice to heal: anemia, liver, skin, kidneys, lymphatic circulation, tiredness, eye, liver, skin problems, detoxification, cancer. Beet juice may kill fungi, is a strong antioxidant and has anti inflammatory propperties.
Important Beet Facts
Beet juice may cause both your stool and urine to turn red. Don't be surprised if this happens!
Beet juice benefits are very powerful. You only need a little bit of juice to get the benefits. Slowly increase the amount from 1 ounce to 2 ounce a week.
Drink the juice raw because the most beneficial substances (like betalains) are lost when cooked. In addition, the oxalic acid in the beet becomes harmful when cooked, but is (in moderation) beneficial when raw(according to juice and nutrition experts Dr Walker, David Wolfe and Gabriel Cousins).
Juice the whole beets: roots plus greens. The greens contain most of the healthy minerals and vitamins.
Reverses Chronic Diseases
The raw oxalic acid in beet juice is known to be a good solvent of inorganic (= bad) calcium deposits in the body. World no 1 raw food teacher David Wolfe suspects that inorganic calcium deposits are the main cause of most chronic diseases. This may explain why beet juice relieves many cases of disease related to calcification in the body, like:
arthritis
heart disease
cancer
kidney stones
eye problems
varicose veins
arteriosclerosis
Like with other bad (or inorganic) calcium dissolvers (MSM, fulvic acid and zeolites), drinking lots of beet juice may result in strong detox symptoms. When calcium dissolves, heavy metals, toxic chemicals, and viruses are released from their "hiding places".
Therefore, it is important to start with small amounts of juice (about 1 ounce). At the same time, boost your immune system by eating a raw food diet (rich in enzymes, super foods, medicinal herbs), eat products that escort (chelate) the toxins safely out of your body (like clay and zeolites) so they wont be reabsorbed and kill viruses and nano bacteria that may be released (like garlic, cats claw, E3 Live, reishi mushroom, etc)
The relatively large amount of magnesium causes the organic (= good) calcium in the leafs to be absorbed well.
Prevents Cancer
One of the huge benefits of beet juice is that research shows the beet to be cancer-preventive. The betacyanin that beet juice contains, helps prevent the formation of cancerous tumors and also detoxifies the body of all harmful toxins.
Together with dissolving the bad calcium these beet juice benefits may be extremely effective in the prevention and possibly reversal of many types of cancer.
There has been research and success with leukemia, colon, lung and skin, liver, and spleen, breast, prostate and testicular cancer. This seems to be the case, even at a very low dose. (Google "beet juice cancer" for more info.)
Prevents Birth Defects
100 grams of beet root provides 27% of the RDA for folic acid known to prevent various birth defects in babies.
Eye Health
Raw beet greens contain two carotenoids: lutein and zeaxanthin. Science reports them to be extremely beneficial for the eye - especially the retina. One of the benefits of beet juice (raw) is that you can absorb the carotenoids easily while maintaining the value - these carotenoids are easily destroyed when cooked.
Anemia
The combination of iron (14% RDA) (a strong oxidant - allows oxygen in the blood) in combination with the antioxidants (127% RDA) (prevent from damage from oxidants) in beet, make iron in beets a valuable source of iron. Therefore, beet juice benefits anemia reversal. (To treat anemia, it is important to also have enough vitamin B12 which is found mostly in animal food and some sea algae e.g. (E3 Live and marine phytoplankton))
Liver Health
The betaine is one of the huge benefits of beet juice. It stimulates the function of liver cells and protects the liver and bile ducts. Beet fiber increased production of detoxifying enzymes in the liver (SOD, catalase, glutathione).
Further beet juice is reported to be excellent in healing gout, kidney and gall bladder. It lowers homocysteine, improves production of stomach acid, reduce serum cholesterol and normalize blood pressure.
Best Way to Enjoy the Benefits of Beet Juice
click on below link
Monday, February 10, 2014
Saturday, February 8, 2014
Posts by : Admin
Eucalyptus Facts and Benefits
Benefits
Eucalyptus oil comes from the dried leaves of the eucalyptus tree. The oil is a colorless liquid with a strong woody and sweet scent. Sauna: Many people add eucalyptus oil to baths, spas and saunas because of its refreshing and antiseptic attributes. Most of the benefits of eucalyptus essential oil can be accessed through the vapor, as well as topical application or ingestion. Therefore, it is commonly used in aromatherapy, which is frequently included in spa treatment packages.
Arterial Vasodilator
Eucalyptus will help dilate the circulatory system, increasing circulation. Use 1 drop during massage over any area of concern.Asthma
During an asthma attack, massage 1-2 drops over the chest. Also, inhale the aroma directly or diffuse in the air.
Brain Blood Flow
Diffuse throughout the home or classroom to increase circulation to the brain.
Bronchitis
Use topically or aromatically, massaging into the chest, back and throat, inhaling from the bottle, or dropping the oil on the shirt collar.
Congestion
Eucalyptus oil uses included clearly congestion from the airways. I recommend inhaling for nasal congestion and massaging the oil over all other affected areas.
Cooling
Yes, eucalyptus oil uses even include cooling the body down. Place several drops in a spray bottle, along with peppermint oil if you'd like some extra oomph, and spritz over the body.
Coughs
Diffuse throughout the room throughout the span of the illness, but also massage into the reflex points of the feet (follow the application guidelines in the link above), as well as over the chest, back, and throat.
Diabetes
Because of the vasodilation mention above, using eucalyptus on a daily basis can increase circulation, a common issue for diabetics. I recommend massaging it into the body with lotion after each shower, as the massage will also help increase circulation.
Disinfectant
Its antiviral and antibacterial properties naturally make cleaning among one of the eucalyptus oil uses. Follow this household cleaners guide for more information.
Emphysema
Eucalyptus oil uses are wonderful for all manner of respiratory disease. Diffuse the oil daily, massage 1 drop over the chest at least once a day, and another drop into the reflex points of the feet.
Expectorant
To help drain mucus from the lungs, massage 1 drop into the reflex points of the feet and apply another drop over the chest at least once a day (I'd personally do three times a day if no sensitivity is found).
Fever
Because eucalyptus oil uses include cooling the body (above), using during a high fever can help the body regulate its temperature and support its efforts in fighting infection.
Flu
Depending on your flu symptoms, eucalyptus oil uses will vary. You can apply to the abdomen to ease diarrhea, massage into aching joints and muscles, or simply diffuse through the air to fight infection.
Hypoglycemia
Another of eucalyptus oil uses, you can help regulate your blood sugar by massaging 1-2 drops into the soles of the feet daily.
Inflammation
Massage 1-2 drops over the afflicted area, always moving toward the heart to support the lymphatic system.
Iris Inflammation
While you should never put essential oils IN the eyes, massaging into the temples may support the irises.
Overexercised Muscles
Strain, fatigue, etc can all be treated with a gentle massage of eucalyptus oil. Always massage toward the heart to move the lactic acid buildup through the lymphatic system.
Pain
Depending on the type of pain, eucalyptus oil uses may necessitate application to the reflex points of the feet or directly over the area of concern.
Pneumonia
Help the lungs to clear by diffusing constantly and massaging directly over the lungs. It will also help to work eucalyptus into the reflex points of the hands and feet.
Respiratory Viruses
Fight viral infections by diffusing eucalyptus constantly during times of illness (read the application guide above for ideas on how).
Rhinitis
Reduce inflammation and open airways by inhaling directly from the bottle, massaging one drop over the sinuses, or applying as a hot compress.
Shingles
Eucalyptus oil uses include shingles for its antiviral properties, as well as its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. Massage into the affected areas daily, add to a warm bath, or use a hot compress over the area.
Sinusitis
Apply as a hot compress over the sinuses and massage 1-2 drops into the reflex points of the feet (toes and pads of the feet). You can also inhale directly or diffuse throughout the room.
Wounds
Eucalyptus essential oil is a good antiseptic owing to its germicidal properties. On its exposure to air, ozone is formed which is a well-known antiseptic. Hence eucalyptus oil is used for healing wounds, ulcers, burns, cuts, abrasions and sores. It is also effective on insect bites and stings.
Other possible eucalyptus oil uses may include: acne treatment, endometriosis, herpes simplex (especially when combined with bergamot), hay fever, blood pressure regulation, and more things related to inflammation, bacterial or viral infection, and pain. It cools the body in summer and protects the body in winter.
Household uses
Add eucalyptus to homemade soaps. It is often found in toothpastes, detergents, and mouthwash. Use it for pet care, such as a flea deterrent for dogs.

Add eucalyptus oil to saunas, spas, and bathtubs to disinfect and refresh. Use to disinfect and deodorize rooms.
Sauna: Many people add eucalyptus oil to baths, spas and saunas due to its refreshing and antiseptic effect.
Usage of eucalyptus oil in aromatherapy is increasing gradually as it also blends well with many other essential oils including thyme essential oil, rosemary essential oil, marjoram essential oil, lavender essential oil, cedarwood essential oil, frankincenseessential oil, etc.
Room freshener: The antiseptic and deodorant nature of eucalyptus oil makes it a perfect room freshener for hospitals and sickbed atmosphere. It also kills bacteria and germs in the air and hence keeps the room environment clean.
Remove tar from clothes or skin harmlessly with this oil as well.
Exceptional germ killer
The most commonly used oil for aromatherapy is eucalyptus globulus, with a strong, camphor-like scent. Others have basically the same traits but are slightly more gentle and include eucalyptus radiata, eucalyptus smithii and eucalyptus citriodora. Whichever species you have or can find, eucalyptus essential oil has especially powerful germicidal properties. For example, place a two percent mixture in an aroma burner to kill 70 percent of staphylococcus bacteria in a room. Another example: researchers in India found eucalyptus to be effective against several strains of E. coli.
Facts
Eucalyptus near Augusta;Western Australia
Eucalyptus /ˌjuːkəˈlɪptəs is a diverse genus of flowering trees and shrubs (including a distinct group with a multiple-stem mallee growth habit) in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae. Members of the genus dominate the tree flora of Australia. There are more than 700 species of eucalyptus, mostly native to Australia, and a very small number are found in adjacent areas of New Guinea and Indonesia. One species, Eucalyptus deglupta, ranges as far north as the Philippines. Only fifteen species occur outside Australia, with just nine of these not occurring in Australia. Species of eucalyptus are cultivated widely in the tropical and temperate world, including the Americas, Europe, Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Middle East, China and the Indian Subcontinent, though most species do not tolerate frost.
Some eucalyptus species have attracted attention from horticulturists, global development researchers and environmentalists because of desirable traits such as being fast-growing sources of wood, producing oil that can be used for cleaning and as a natural insecticide, or an ability to be used to drain swamps and thereby reduce the risk of malaria. Outside their natural ranges, eucalyptus are both lauded for their beneficial economic impact on poor populations and criticized for being "water-guzzling" aliens, leading to controversy over their total impact.
On warm days eucalyptus forests are sometimes shrouded in a smog-like mist of vaporized volatile organic compounds (terpenoids); the Australian Blue Mountains take their name from the haze.
Nearly all eucalyptus are evergreen but some tropical species lose their leaves at the end of the dry season. As in other members of the myrtle family, eucalyptus leaves are covered with oil glands. The copious oils produced are an important feature of the genus. Although mature Eucalyptus trees are usually towering and fully leafed, their shade is characteristically patchy because the leaves usually hang downwards.
The most readily recognizable characteristics of eucalyptus species are the distinctive flowers and fruit (capsules or "gumnuts").
Eucalyptus pauciflora are frost intolerant, capable of withstanding cold and frost down to about
−20 °C (−4 °F)
Most eucalyptus are not tolerant of frost, or only tolerate light frosts down to −5 °C (23 °F); the hardiest are the so-called snow gums, such as Eucalyptus pauciflora, which is capable of withstanding cold and frost down to about −20 °C (−4 °F). Two subspecies, E. pauciflora subsp. niphophila and E. pauciflora subsp. debeuzevillei in particular are even hardier and can tolerate even quite severe winters. Several other species, especially from the high plateau and mountains of central Tasmania such as Eucalyptus coccifera, Eucalyptus subcrenulata and Eucalyptus gunnii, have also produced extreme cold-hardy forms and it is seed procured from these genetically hardy strains that are planted for ornament in colder parts of the world.
Phascolarctos cinereus (koala) ready to eat Eucalyptus leaves
An essential oil extracted from eucalyptus leaves contains compounds that are powerful natural disinfectants and can be toxic in large quantities. Several marsupial herbivores, notably koalas and some possums, are relatively tolerant of it. The close correlation of these oils with other more potent toxins called formylated phloroglucinol compounds (euglobals, macrocarpals and sideroxylonals) allows koalas and other marsupial species to make food choices based on the smell of the leaves. For koalas, these compounds are the most important factor in leaf choice.
Sugar glider drinking nectar of the Eucalyptus ptychocarpa
Eucalyptus flowers produce a great abundance of nectar, providing food for many pollinators including insects, birds, bats and possums. Although eucalyptus trees are seemingly well-defended from herbivores by the oils and phenolic compounds, they have insect pests. These include the eucalyptus longhorn borer Phoracantha semipunctata and the aphid-like psyllids known as "bell lerps", both of which have become established as pests throughout the world wherever eucalypts are cultivated.
Eucalyptus Oil
Eucalyptus oil is readily steam distilled from the leaves and can be used for cleaning and as an industrial solvent, as an antiseptic, for deodorising, and in very small quantities in food supplements, especially sweets, cough drops, toothpaste and decongestants. It has insect repellent properties and is an active ingredient in some commercial mosquito repellents. Eucalyptus globulus is the principal source of eucalyptus oil worldwide.
Eucalyptus Honey. The nectar of some eucalyptus produces high-quality monofloral honey.
Dyeing using eucalyptus.
All parts of Eucalyptus may be used to make dyes that are substantive on protein fibers (such as silk and wool), simply by processing the plant part with water. Colors to be achieved range from yellow and orange through green, tan, chocolate and deep rust red. The material remaining after processing can be safely used as mulch or fertilizer.
One way in which the eucalyptus, mainly the blue gum E. globulus, proved valuable in California was in providing windbreaks for highways, orange groves, and other farms in the mostly treeless central part of the state. They are also admired as shade and ornamental trees in many cities and gardens.
Sunday, January 26, 2014
Posts by : Admin
Living off the Grid - Earthships
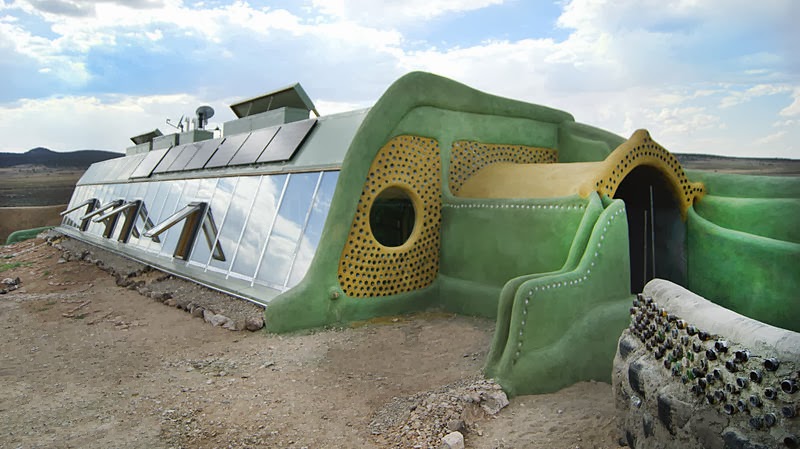
An Earthship is a type of passive solar house made of natural and recycled materials (such as earth-filled tires), designed and marketed by Earthship Biotecture of Taos, New Mexico. The term is a registered trademark of Michael Reynolds.
 |
| Michael Reynolds (1975) |
 | ||
| G2 Global model Earthship Taos N.M.., | South and east side of an Earthship passive solar home. |
Earthships are primarily designed to work as autonomous buildings using thermal mass construction and natural cross ventilation assisted by thermal draught (Stack effect) to regulate indoor temperature. Earthships are generally off-the-grid homes, minimizing their reliance on public utilities and fossil fuels. Earthships are built to utilize the available local resources, especially energy from the sun. For example, windows on sun-facing walls admit lighting and heating, and the buildings are often horseshoe-shaped to maximize natural light and solar-gain during winter months. The thick, dense outer walls provide thermal mass that naturally regulates the interior temperature during both cold and hot outside temperatures.
 |
| Internal, non-load-bearing walls are often made of a honeycomb of recycled cans joined by concrete and are referred to as tin can walls. |
Internal walls are usually thickly plastered with adobe. Tin can walls can also be used on top of the tire walls ("can and concrete bond beams") as an alternative to wooden shoes. An alternative to these concrete bond beams are wooden bond beams with wooden shoes. The wooden shoes are made using wooden shimming blocks (of 6x6x8' dimensions) placed on top of the wooden bond beam (the latter is basically just 2 layers of 2x12 lumber bolted on concrete anchors (poured blocks of concrete located inside the top tyres). Some rebars are used to "nail" the wooden shoes to the wooden bond beam. The tire walls are additionally strengthened by using concrete in the tires on the ends (called "concrete half blocks"). The roof is made using trusses or vigas (wooden support beams) which rest on the wooden shoes (or tin can walls) placed on the wooden (or concrete) bond beams. The roof as well as the north, east and west facing walls of an Earthship are also heavily insulated to prevent heat loss.
Michael Reynolds' first building, the Thumb House. Built in the early 1970s, it incorporated designs found in later Earthships
The Earthship as it exists today, began to take shape in the 1970s. Mike Reynolds, founder of Earthship Biotecture, a company that specializes in designing and building Earthships, wanted to create a home that would do three things; first, it would be sustainable architecture, using material indigenous to the entire planet as well as recycled materials wherever possible. Second, the homes would rely on natural energy sources and be independent from the "grid", therefore being less susceptible to natural disasters and free from the electrical and water lines that Reynolds considered unsightly and wasteful. Finally, it would be economically feasible for the average person with no specialized construction skills to be able to create.
A building being built of cans in the 1970s
The design used with most earthships. A large series of windows and the use of tires characterize the earthsheltered building
Eventually, Reynolds' vision took the form of the common U-shaped earth-filled tire homes seen today. As a concept, the Earthship was not limited to tires – any dense material with a potential for thermal mass, such as concrete, adobe, earthbags, or stone could theoretically be used to create a building similar to an Earthship.
 |
| The earth-rammed tire is used in the vast majority of Earthships. |
Rammed-earth and tires are easily accessible and allow for owner build structures and use of untrained labour. Scrap tires are plentiful around the world and easy to come by; there are an estimated 2 billion tires throughout the United States. As of 1996, as many as 253 million scrap tires were being generated each year in the United States, with 70% being reclaimed by the scrap tire market (leaving perhaps 75 million scrap tires available for reuse as whole tires).[1] The method by which scrap tires are converted into usable "bricks" (the ramming of the earth) is simple and affordable but labour intensive.
The earth-rammed tires of an Earthship are usually assembled by teams of two people working together as part of a larger construction team. One member of the two person team shovels dirt, which usually comes from the building site, placing it into the tire one scoop at a time. The second member, who stands on the tire, uses a sledge hammer to pack the dirt in. The second person moves in a circle around the tire to keep the dirt even and avoid warping the tire. These rammed earth tires in an Earthship are made in place since they can weigh as much as 300 pounds and therefore can be difficult to relocate.
Additional benefits of the rammed earth tire are its high load-bearing capacity and its resistance to fire.
A fully rammed tire, which is about 2 feet 8 inches wide, is massive enough to surpass conventional requirements for structural load distribution to the earth. Because the tire is full of soil, it does not burn when exposed to fire. In 1996 after a fire swept through many conventional homes in New Mexico, an Earthship discovered in the aftermath was relatively unharmed. Only the south-facing wall and the roof had burned away.
Currently, Earthships are in use in almost every state in the United States and Canada, as well as many European countries. The colder climates require the use of strong insulation on the outside of the tire walls, which was not common in earlier designs. Building an Earthship in a Cold Climate? Earthships are continually being built around the world by Taos based Earthship Biotecture. In addition, books, plans and training sessions (Earthship Academy) are made available by Reynolds. This owner builder approach together with the use of inexpensive materials has inspired people worldwide to build their own passive solar homes.
Systems
The Earthship was designed as a structure that would be free of the constraints of centralized utilities, on which most modern shelters rely. Earthships must be able to create their own utilities, and to utilize readily available sustainable materials. In order to be entirely self-sufficient, the Earthship needs to be able to handle the three systems of water, electricity, and climate.
Water
 |
A domestic rainwater harvesting system
|
Collection
Earthships are designed to catch and use water from the local environment without bringing in water from a centralized source. Water used in an Earthship is harvested from rain, snow, and condensation. As water collects on the roof, it is channeled through a silt-catching device and into a cistern. The cisterns are positioned so they gravity-feed a WOM (water organization module) that filters out bacteria and contaminants and makes it suitable for drinking. The WOM consists of filters and a DC-pump that are screwed into a panel. Water is then pushed into a conventional pressure tank to create common household water pressure.
Water collected in this fashion is used for every household activity except flushing toilets. The water used for flushing toilets has been used at least once already: frequently it is filtered waste-water from sinks and showers, and described as "Greywater".
Greywater
Greywater, used water that is unsuitable for drinking, is used within the Earthship for a multitude of purposes. First, before the greywater can be reused, it is channeled through a grease and particle filter/digester and into a 30"-60" deep rubber-lined botanical cell, a miniature living machine, within the Earthship. With embedded plants, this filter also potentially can be used to produce food (for example, by using a fruit tree).
Oxygenation, filtration, transpiration, and bacteria-encounter all take place within the cell and help to cleanse the water. Within the botanical cell, filtration is achieved by passing the water through a mixture of gravel and plant roots. Because of the nature of plants, oxygen is added to the water as it filters, while nitrogen and phosphate is removed. Note that plant root cells do not produce oxygen but consume it; only the leaves of plants produce oxygen. Water taken up through the plants and transpired at their tops helps to humidify the air. In the cell, bacteria will naturally grow and help to cleanse the water.
Water from the low end of the botanical cell is then directed through a peat-moss filter and collected in a reservoir or well. This reclaimed water is then passed once more through a greywater board and used to flush conventional toilets.
Often, greywater made at earthships is not polluted enough to justify treatment (its "pollution" being usually just soap, which is often not environmentally damaging). At earthships, plants are placed at outlets of fixtures to regain the water and the nutrients lost (e.g. from the soaps). Usually, a single plant is placed directly in front of the pipe, but mini drain-fields are also sometimes used. The pipe is made large enough (5,08 cm) so that the formation of underground gas (from the greywater) is avoided. This is done with kitchen and bathroom sinks, and even showers, washing machines, and dishwashing machines. The plants are usually placed indoors with the sinks and outdoors with the washing/dishwashing machines and shower (to avoid indoor "floods"). Also, with the latter, larger drain-fields are used instead of a mere plant being placed before an outlet.
 | |
| Black Water - | The water system with integrated flush toilet, as used in most earthships |
Black water
Black water, water that has been used in a toilet, was usually not created within many of the earliest earthships as the use of conventional toilets was discouraged. Instead, in the early days composting toilets were advocated, which use no water at all. However, with the new greywater treatment system design (as used in Nautilus and Helios) created by Michael Reynolds, flush toilets have now found a place in the earthship and the general water system has been redesigned according to the new "6-step process".
Now, when the newly included flush-toilets are used, blackwater is not reused within the Earthship. Instead, blackwater is sent to a solar-enhanced septic tank with leach-field and planter cells (the whole being often referred to as the "incubator"). The solar-enhanced septic tank is a regular septic tank which is heated by the sun and glazed with an equator-facing window. The incubator stores the sun's heat in its concrete mass, and is insulated, to help the anaerobic process. Water from the incubator is channeled out to an exterior leach field and then to landscaping "planter cells" (spaces surrounded by concrete in which plants have been put). The cells are similar to the botanical cell used in greywater treatment and are usually placed just before and under the windows of the earthship.
In cases where it is not possible to use flush-toilets operating on water, dry solar toilets are now advocated, instead of regular composting toilets. If this is the case, no black water is formed and the use of an incubator is thus (usually) not necessary. Instead, regular "planters" (plants used for sucking up water/nutrients) are then used. When using regular planters as well, no chemical soaps or detergents can be used.
The space where the WOM (water organization module), graywater pump panel, pressure tank, (first set of) batteries, and POM (power organising module) are stored is in a small room referred to as the "systems package".
 |
| Self-sufficient, Sustainable, Water Collection to use and renew, sun & wind generate electricity, recycled building materials, |
Electricity
Earthships are designed to collect and store their own energy from a variety of sources. The majority of electrical energy is harvested from the sun and wind. Photovoltaic panels and windturbines located on or near the Earthship generate DC energy that is then stored in several types of deep-cycle batteries. The space in which the batteries are kept is usually a special, purpose-built room placed on the roof. Additional energy, if required, can be obtained from gasoline-powered generators or by integrating with the city grid.
In an Earthship, a Power Organizing Module is used to take stored energy from batteries and invert it for AC use. The Power Organizing Module is a prefabricated system provided by Earthship Biotecture that is simply attached to a wall on the interior of the Earthship and wired in a conventional manner. It includes the necessary equipment such as circuit breakers and converters. The energy run through the Power Organizing Module can be used to run any house-hold appliance including washing machines, computers, kitchen appliances, print machines, and vacuums. Ideally, none of the electrical energy in an Earthship is used for heating or cooling.
 |
| Drainage Channel, Sunlight |
Climate
The interior climate of an Earthship is stabilized by taking advantage of natural phenomena. Mainly, the Earthship is designed to use the properties of thermal mass and passive solar heating and cooling. Examples are large front windows with integrated shades, trombe walls and other technologies such as skylights or Steve Baer's "Track Rack" solar trackers (doubling as an energy generation device and passive solar source).
The load-bearing walls of an Earthship, which are made from steel-belted tires rammed with earth, serve two purposes. First, they hold up the roof, and second, they provide a dense thermal mass that will soak up heat during the day and radiate heat during the night, keeping the interior climate relatively comfortable all day.
In addition to high thermal mass, some Earthships may be earth-sheltered. The benefits of earth-sheltering are twofold because it adds to the thermal mass and, if the Earthship is buried deep enough, allows the structure to take advantage of the Earth's stable temperature.
The Earthship is designed in such a way that the sun provides heating, ventilation, and lighting. To take advantage of the sun, an Earthship is positioned so that its principal wall, which is nonstructural and made mostly of glass sheets, faces directly towards the equator. This positioning allows for optimum solar exposure.
To allow the sun to heat the mass of the Earthship, the solar-oriented wall is angled so that it is perpendicular to light from the winter sun. This allows for maximum exposure in the winter, when heat is wanted, and lesser exposure in the summer, when heat is to be avoided. Some Earthships, especially those built in colder climates, use insulated shading on the solar-orientated wall to reduce heat loss during the night.
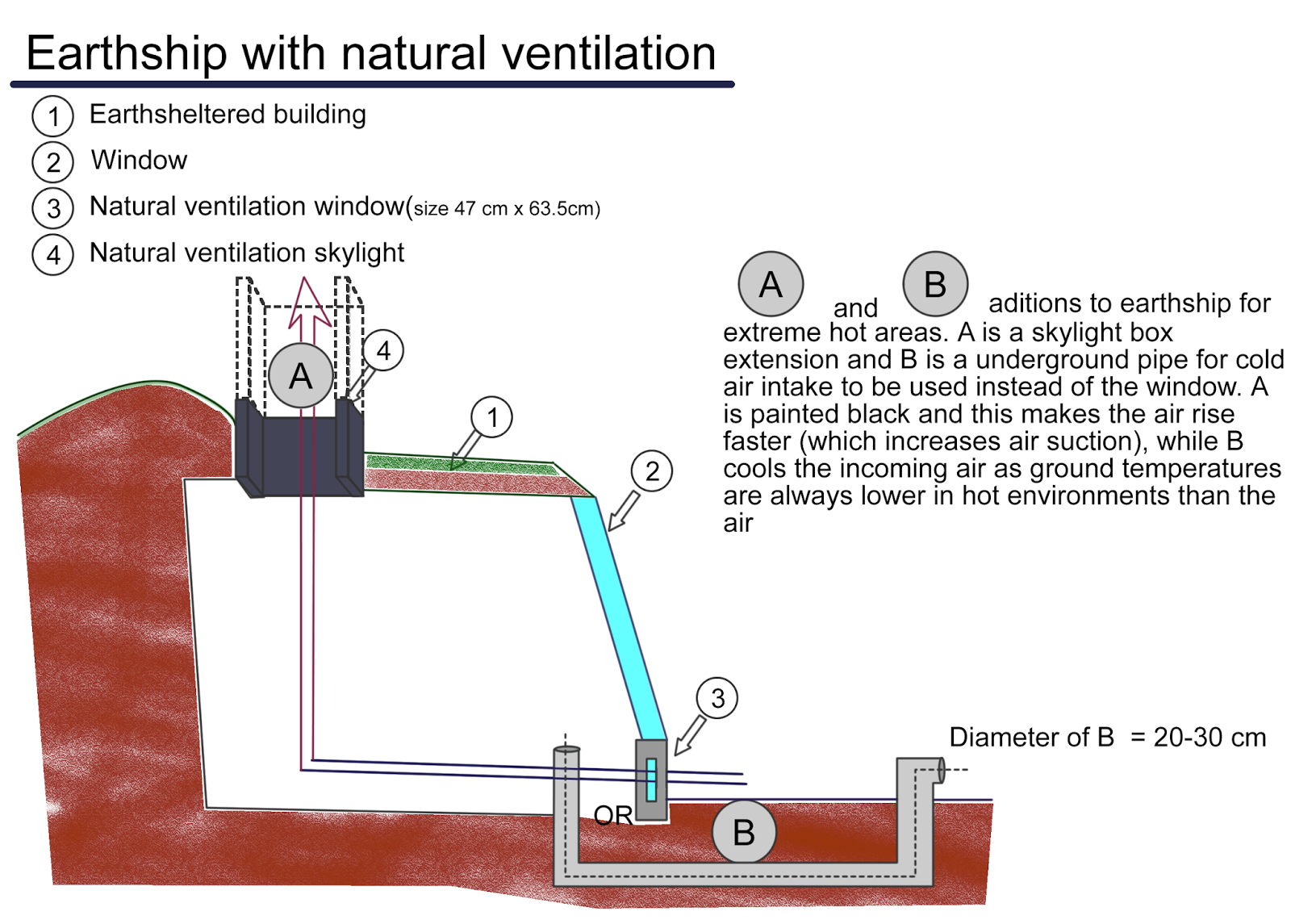 |
Natural ventilation
Natural convection cooling an Earthship
The earthships usually use their own natural ventilation system. It consists of cold(er) air coming in from a front ("hopper") window, especially made for this purpose and flowing out through (one of) the skylights that are placed on the earthship. As the hot air rises, the system creates a steady airflow - of cooler air coming in, and warmer air blowing out.
 |
| Earth Tubes |
Heating problems
Earthships rely on a balance between the solar heat gain and the ability of the tire walls and subsoil to transport and store heat. The design intends to require little if any auxiliary heat. Some earthships have suffered from overheating and some from overcooling.
Some earthships appear to have serious problems with heat loss. In these cases heat appears to be leaking into the ground constantly during the heating season and being lost. This situation may have arisen from the mistaken belief that ground-coupled structures (building in thermal contact with the ground) do not require insulation. The situation may also be due to large climatic differences between the sunny, arid, and warm Southwest (of the USA) where earthships were first built and the cloudier, cooler, and wetter climates where some are now being built. Malcolm Wells, an architect and authority on earth-sheltered design, recommends an imperial R-value 10 insulation between deep soils and heated spaces. Wells's insulation recommendations increase as the depth of the soil decreases.
In very limited and specific situations, uncommon during the heating season, thermal mass can marginally increase the apparent R-value of a building assembly such as a wall. Generally speaking thermal mass and R-value are distinct thermodynamic properties and should not be equated. Thermal performance problems apparently seen in some earthship designs may have occurred because of thermal mass being erroneously equated to R-value. The imperial R-value of soil is about 1 per foot.
Africa
The first earthship in South Africa was built by Angel and Yvonne Kamp from 1996 to 1998. They rammed a total of 1,500 tires for the walls. The earthship, near Hermanus, is located in a 60 hectare private nature reserve which is part of a 500000 hectare area enclosed in a game fence and borders the Walker Bay Nature Reserve.
The second earthship in South Africa is a recycling centre in Khayelitsha run as a swop shop concept. The centre was finished in December 2010.Another low cost house built with tyres is in development in Bloemfontein.
A project nearing completion in South Africa is a combined living quarters for 4 to 5 people, a bed and breakfast, and an information/training centre in Orania.This earthship is based on the global earthship model and is built with a foundation of tyres, has roof bearing walls built with earthbags, and interior walls built with cob, cans and plastic bottles. This earthship adheres to all six principles of an earthship. This is the largest earthbag earthship in the world.
A residential house is in the planning phase for Swaziland.
In 2011, construction began on the Goderich Waldorf School of Sierra Leone. The school was the first educational institution to use earthship architecture. Although Mike Reynolds and a team of interns helped complete the first two classrooms, the majority of the building was built by community members who had been trained in Reynolds' building techniques.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)














.jpg)























